-
tel: +8617802596658
-
email: shpowderseparator@gmail.com
-
Whatsapp: 8617802599580






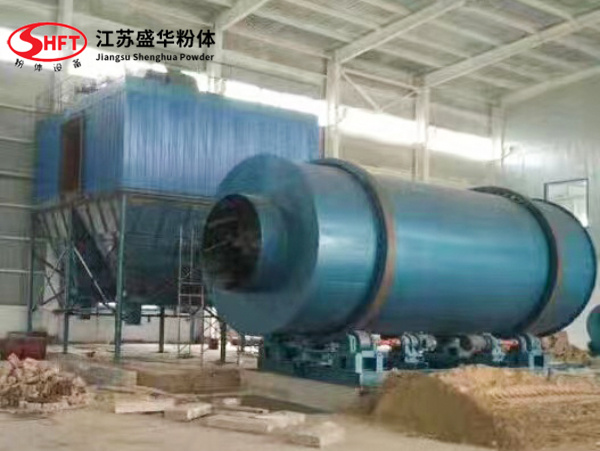
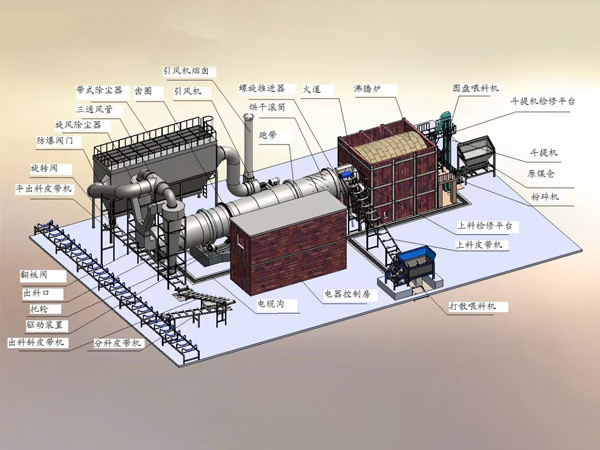
A dryer is a mechanical device used to remove excess moisture from materials. It plays an important role in many industries, especially in the fields of textiles, agriculture, chemicals, and food processing.
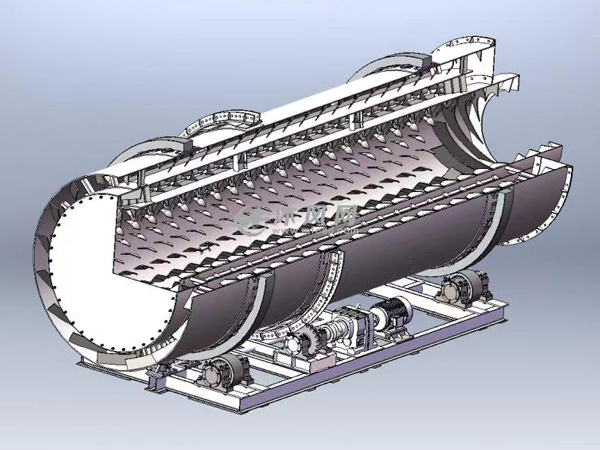
The working principle of a dryer usually involves the transfer of heat energy. The material is fed into the dryer and heated by hot air, steam, or other heat sources to evaporate the water in the material. The evaporated water is then discharged from the dryer, and the dry material is discharged from another outlet.
There are many types of dryers, including drum dryers, belt dryers, fluidized bed dryers, etc. Each type of dryer has its specific application scenarios and advantages. For example, drum dryers are suitable for processing granular or block materials, while belt dryers are more suitable for processing flakes or films.
In the agricultural field, dryers are widely used to dry grains and seeds to ensure their quality during storage and transportation. In the textile and chemical industries, dryers are used to process cloth, fibers, chemicals, etc. In the food processing industry, dryers are used to remove excess moisture from food to extend its shelf life.
In short, the dryer is an important mechanical equipment, which provides great convenience for the production and processing processes of various industries by removing excess moisture from the materials.
 |
 |
















